The following is a list of reasons for goiters to develop:
Iodine deficiency – Iodine is an essential component of thyroid hormones. In areas where iodine is deficient, there will be less thyroid hormones (T3 & T4) in the blood stream. As a consequence, the pituitary gland will produce more TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormones), TSH in turn stimulates the thyroid gland to work harder to make hormones and over time stimulates it to get bigger. Uncommon in the countries that use iodized salt, like the US.
areas where iodine is deficient, there will be less thyroid hormones (T3 & T4) in the blood stream. As a consequence, the pituitary gland will produce more TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormones), TSH in turn stimulates the thyroid gland to work harder to make hormones and over time stimulates it to get bigger. Uncommon in the countries that use iodized salt, like the US.
Inflammation – Thyroiditis is an inflammatory condition that causes the thyroid gland to swell, and become painful. It also can cause the gland to work less and produce less hormone.
Hashimoto’ s Disease – Also called Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis is an immune condition when the immune system by mistake attacks the thyroid causing it to work less with each attack. Pituitary gland senses the decreased T3 & T4 levels and produces excess TSH which cause the thyroid to grow in time.
Grave’s Disease – This condition is caused by the immune system producing an antibody (TSI – Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulin), that attaches to the same area that TSH would attach and stimulates the thyroid to not only release more hormone but also grow. These patient have symptoms of hyperthyroidism along with goiter.
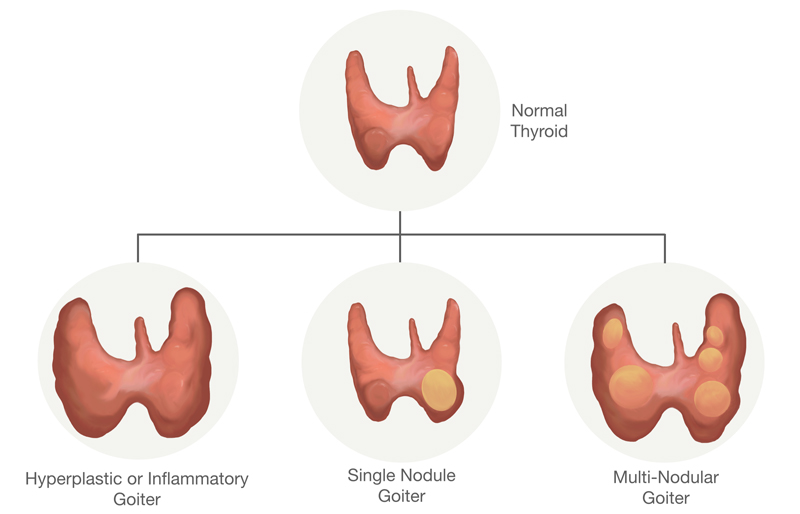
Single Thyroid – When a nodule gets large enough to make the thyroid bigger, wider, or longer then it is considered to be a goiter. These nodule can be benign (adenoma) or malignant (carcinoma).
Single Thyroid – When a nodule gets large enough to make the thyroid bigger, wider, or longer then it is considered to be a goiter. These nodule can be benign (adenoma) or malignant (carcinoma).
Multinodular Goiter – This occurs when there are multiple nodules which can cause one or both sides of the thyroid to get bigger.
Symptoms
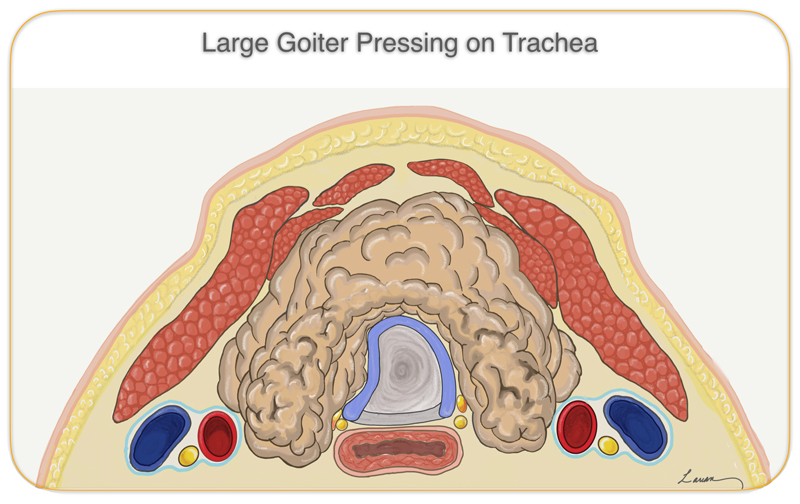
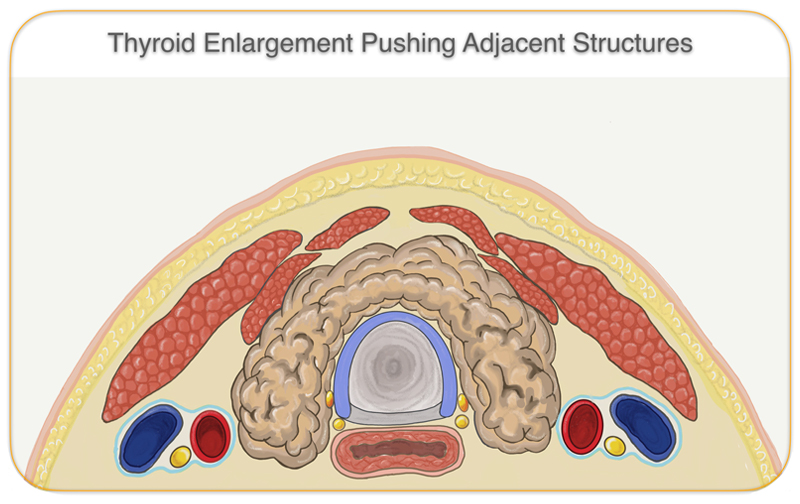
A goiter that is small and not pressing on the surrounding tissue is usually not a problem, unless the amount of hormones it produces is too low or excessive. Larger goiters can press on the breathing tube (trachea) or swallowing tube (esophagus), which may lead to shortness of breath, coughing or difficulty swallowing.


 areas where iodine is deficient, there will be less thyroid hormones (T3 & T4) in the blood stream. As a consequence, the pituitary gland will produce more TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormones), TSH in turn stimulates the thyroid gland to work harder to make hormones and over time stimulates it to get bigger. Uncommon in the countries that use iodized salt, like the US.
areas where iodine is deficient, there will be less thyroid hormones (T3 & T4) in the blood stream. As a consequence, the pituitary gland will produce more TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormones), TSH in turn stimulates the thyroid gland to work harder to make hormones and over time stimulates it to get bigger. Uncommon in the countries that use iodized salt, like the US.